In the Neurourbanism study, we are measuring brain activity before and after what we call a “Nature-based Intervention” at specific sites. We have selected your neighbourhood as one of our study sites. We will collect data in two phases: first, before the intervention (in 2025), and then after (in 2027). Both times, we will be following Read More
Tag: research
Calling Nova Gorica locals!
Launching the recruitment for participants of the NUA study in Nova Gorica for April/May 2025! Sign and and help up shape mental health and well-being!
Network Nature Annual Event
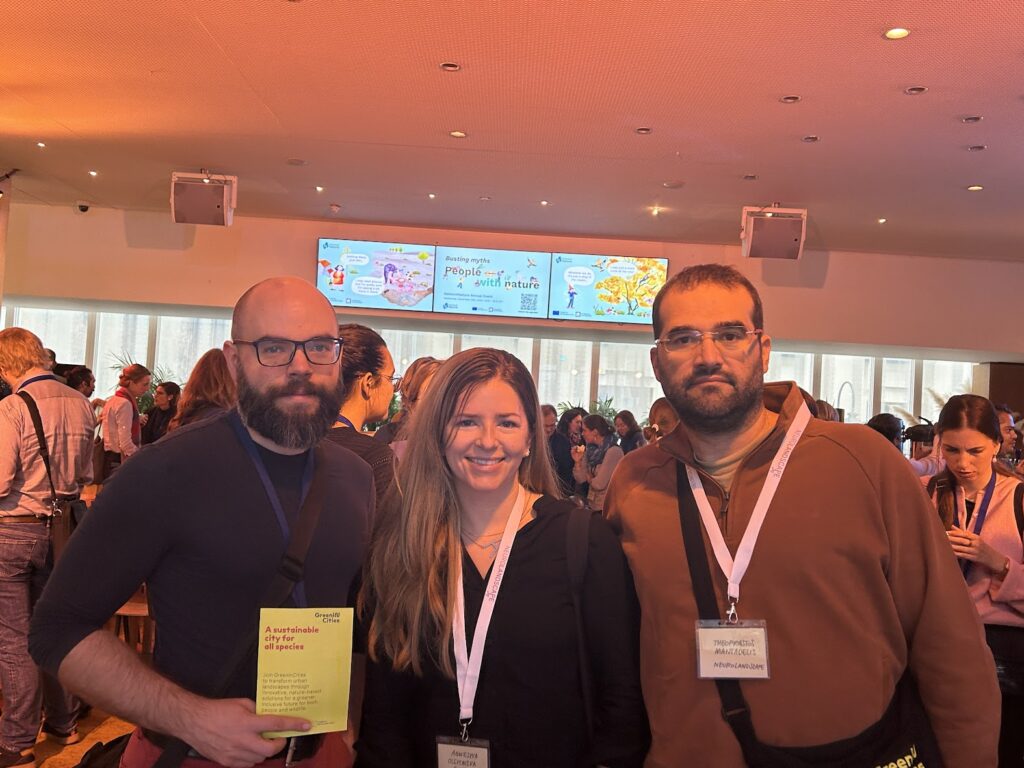
NetworkNature Annual Event 2024 | Busting myths: People with nature 24-25 of September, 2024 | Brussels, Belgium The NeuroLandscape team just returned from an incredible few days at the NetworkNature EU Annual Event in Brussels! What a wonderful blend of insightful discussions, knowledge-rich myth-busting panels, and interactive hands-on workshops, all reinforcing the key message of Read More
Nature in Mind: An Interview with Dr. Anna María Pálsdóttir
Dr. Anna María Pálsdóttir is the Senior Lecturer/Assistant Professor in Environmental Psychology at the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences (SLU), the Department of People and Society. She is a professional horticulturist with a BSc in Biology & Horticulture Sciences and a MSc and PhD in Landscape Planning and Environmental Psychology. Dr. Pálsdóttir works with conceptual Read More
Building Back Differently: The Role of CLM in Public Health Promotion through Nature-based Solutions
“The future of humanity is undoubtedly urban,” warns the UN-Habitat in their World Cities Report (2022), urging public health policies to address the growing health risks associated with urban expansion. Urban environments — characterized by traffic, pollution, noise, and overcrowding — not only create fertile ground for physical health issues but also place a significant Read More
NeuroLandscape a part of GreenME – the Horizon EU Funded Project!
NeuroLandscape is delighted to announce its participation in the consortium selected for the prestigious Horizon Europe GreenME project with a budget of nearly 6M euro. This collaboration presents an exciting opportunity to advance our mission of integrating nature-based solutions into urban environments for enhanced well-being and sustainable living. Led by Universita Autonoma de Barcelona, the Read More
EDRA52 Conference Presentation | Just Environments
Speech presented at the 25th Environmental Design Research Association 25th Conference in the panel “Green Resilience and Behaviour” by Nazwa Tahsin. Part of the Research Program “Nature Connection and Mental Health of Communities”. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hwGBP0sscNo&t=24s https://cdn.ymaws.com/www.edra.org/resource/resmgr/edra52/subpages/edra52_-_program_book.pdf
Simply Green is Simply not Enough – a Prelude to Mentally Healthy Cities
The fast-paced urbanization and disconnection of people from nature and the current series of lockdowns, contribute to an increasing burden of mental health disease in cities. Researchers have estimated that it is 39% more likely to develop depression when living in urbanized areas as compared to rural regions [source]. Other mental illnesses and neurodegenerative disorders Read More
NeuroLandscape featured in BBC “My Perfect City”
NeuroLandscape featured in BBC “My Perfect City” Series episode which was released on: 30 Dec 2020 New episode of the BBC World Service “My perfect city” features Dr Agnieszka Olszewska-Guizzo among other experts. They discuss Singapore as a city which attempts to improve residents’ mental wellbeing through urban design. Generally, people in cities are likely Read More
Healthy Cities – Cities for Humans, Conscious Warsaw 2020 (VIDEO)
A speech presented during the “Conscious Warsaw – Sensing our City” webinar organized by the Center for Conscious Design, which took place on October 22, 2020, in Polish (English subtitles available in this video!). Dr. Agnieszka Olszewska-Guizzo presented a new concept of designing mentally healthy cities based on contact with salutogenic natural landscapes (Contemplative Landscapes) Read More