A recent publication tackling the intersection of climate change and health, developed by members of the NeuroLandscape team, has been released in the book Climate Change and Health Hazards: Addressing Hazards to Human and Environmental Health from a Changing Climate, edited by Walter Leal Filho, Diogo Guedes Vidal, and Maria Alzira Pimenta Dinis. The chapter, Read More
Tag: bangladesh
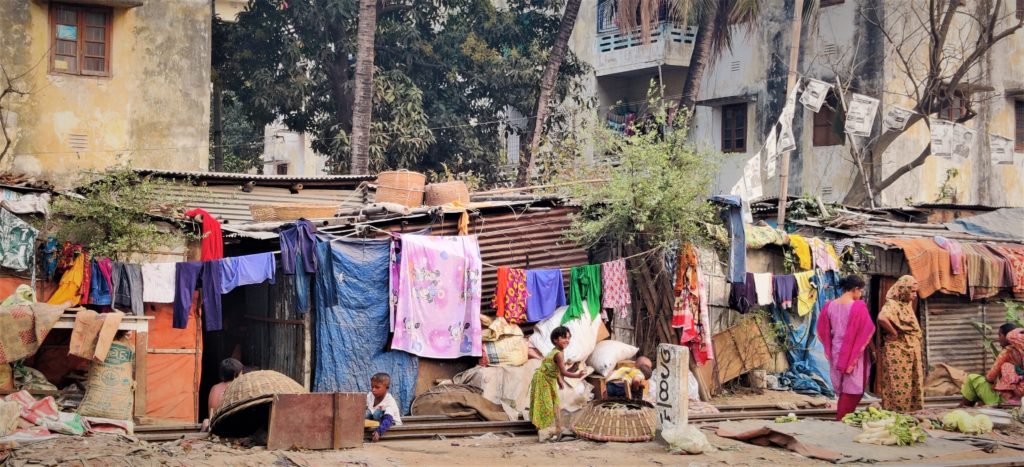
Mental Health in Slums – the Case of Bangladesh Among Other Developing Countries
The share of the world’s population living in urban areas has been predicted to increase from 55% in 2018 to 60% in 2030 (UN, 2018). Every year people move to the urban areas from villages for various reasons. If we try to see this urban-rural migration under the push-pull model, push factors from rural end Read More
EDRA52 Conference Presentation | Just Environments
Speech presented at the 25th Environmental Design Research Association 25th Conference in the panel “Green Resilience and Behaviour” by Nazwa Tahsin. Part of the Research Program “Nature Connection and Mental Health of Communities”. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hwGBP0sscNo&t=24s https://cdn.ymaws.com/www.edra.org/resource/resmgr/edra52/subpages/edra52_-_program_book.pdf
Policy Briefs – Urban Health and Wellbeing Programme by Springer
In our most recent contribution to the Volume Two of the book series Urban Health and Wellbeing Systems Approaches, published by Springer and Zhejian University, we discuss the preliminary findings of our research project currently conducted in low-income communities in Medellin Colombia for our program Planting Seeds of Empowerment: Mental Health and Wellbeing of the Read More
The New Urban Normal_Dr Diana’s speech at TecNM (Mexico)_VIDEO
24th September 2020. Tecnológico Nacional de México, campus Costa Grande, hosted an online event addressing the World New Normal in the interdisciplinary lens. Dr Diana Benjumea gave a speech regarding architecture and urban planning, where she sets a new paradigm of bottom-up, evidence-based urban design. Moreover, she introduces NeuroLandscape projects and explains the global implications Read More
Unraveling links among climate change, poverty and health in slums of Dhaka
It is well known to the environmentalists that Bangladesh is currently considered the 7th most vulnerable country to the adverse effects of ongoing climate change. What we do not know, however, is the adverse effects that are already in place and how much it is tangled with rural-urban migration, rehabilitation, gender, human rights, and health Read More